Leader: Czech Centre for Science and Society
Contact person: RNDr. Karel Charvát, charvat@ccss.cz
Visit Inspire4Youth’s NEW Facebook page!
Open INSPIRE4Youth supports creativity, technical capabilities, skills, knowledge and also relations, through the sharing of spatial based content and educational materials around environment. Using new methods of digital cartography enables to go beyond linguistic barriers. Using principles of Linked Open Data INSPIRE4Youth offer new possibilities of analyzing relation among different types of objects.
The pilot is focused on building of Environmental and Geographical Web based atlas and educational quizzes based on utilization of Geospatial data, Linked Open data and other environmental data (maps) for educational and gaming purposes. The main components of the environment introduced are – water, air, soil, forests, nature protection, climate information, landscape, waste management, forest management etc. Each component has its actual condition measured for the region. All this will be made available in an entertaining manner – no school textbooks. Pilot also re uses database of Smart Point of Interest from Smart Tourist Data pilot. The main user group for this Atlas are students – higher grades of elementary schools, high schools and universities. However it should be appealing also for any adult person interested in topic.
The pilot currently cover two pilot solution with tree different applications:
- Thematic Environmental Map Atlas based on Map Composer and Mobile Thematic Map Viewer
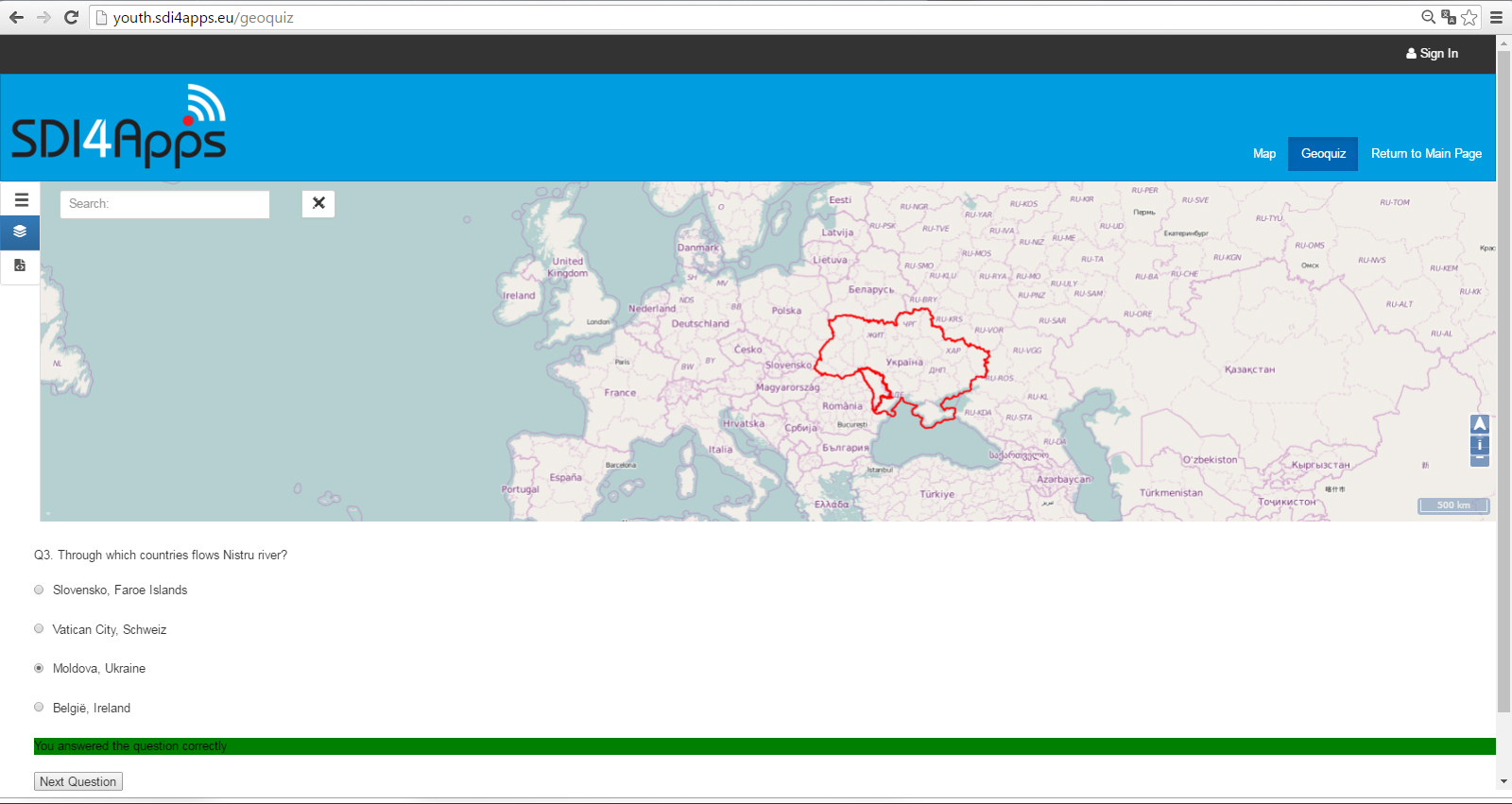
- Geographical quiz based on database of Linked Open Data
User engagement
The identified stakeholder group are:
- Schools and students.
- Public bodies – European, national and regional education and environmental authorities.
- Experts – Education and environmental experts, researchers & decision makers.
- Enterprises, Companies, NGOs and SMEs – targeting and working with young people.
- Citizens – young people.
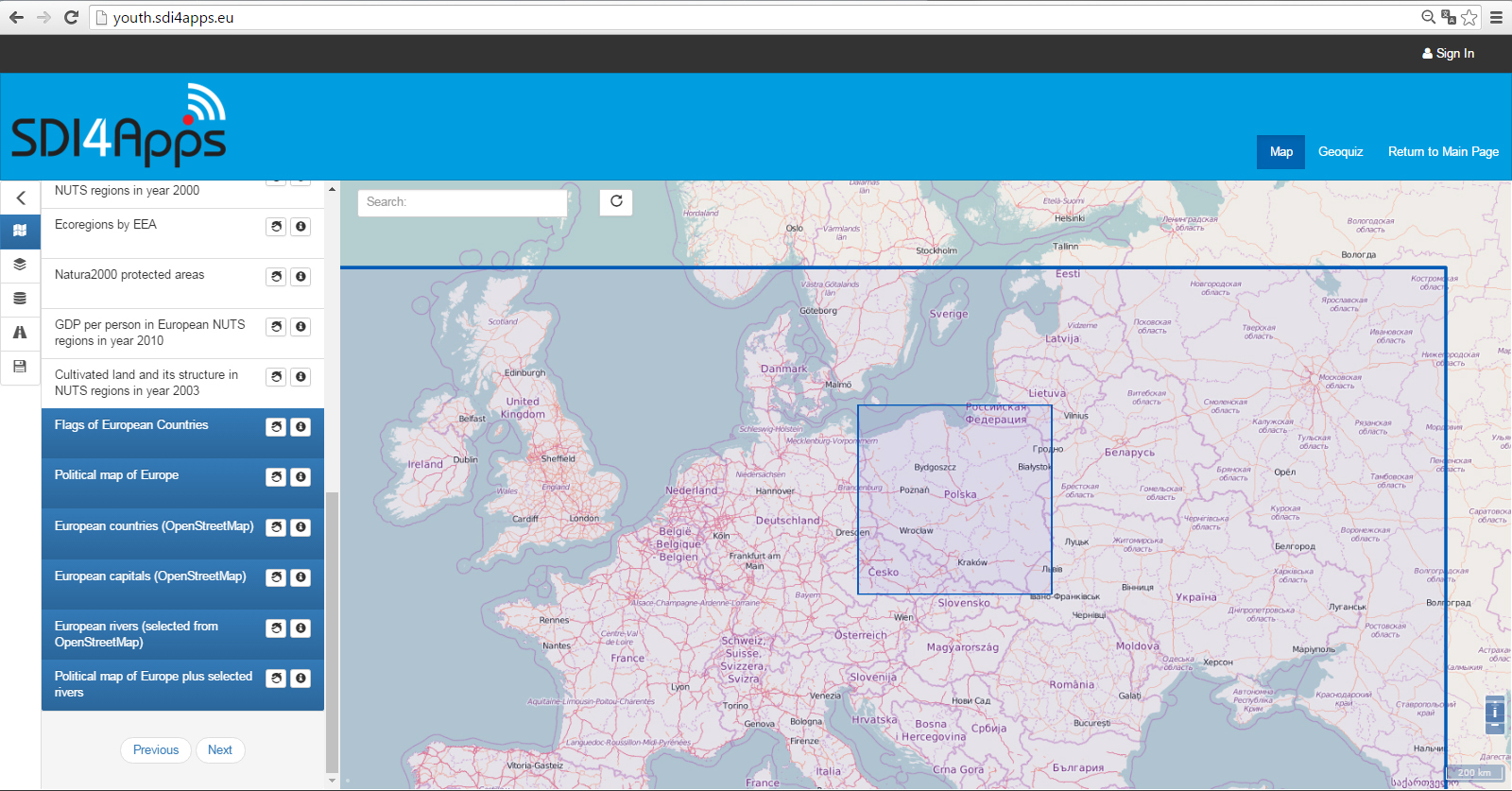
Thematic Environmental Map Atlas
Thematic Map atlas offers:
- Thematic maps and additional information (tables, graphs, charts…)
- Thematic maps created by simple tools by users:
- by using own data collected through mobile apps
- from simple shared tables
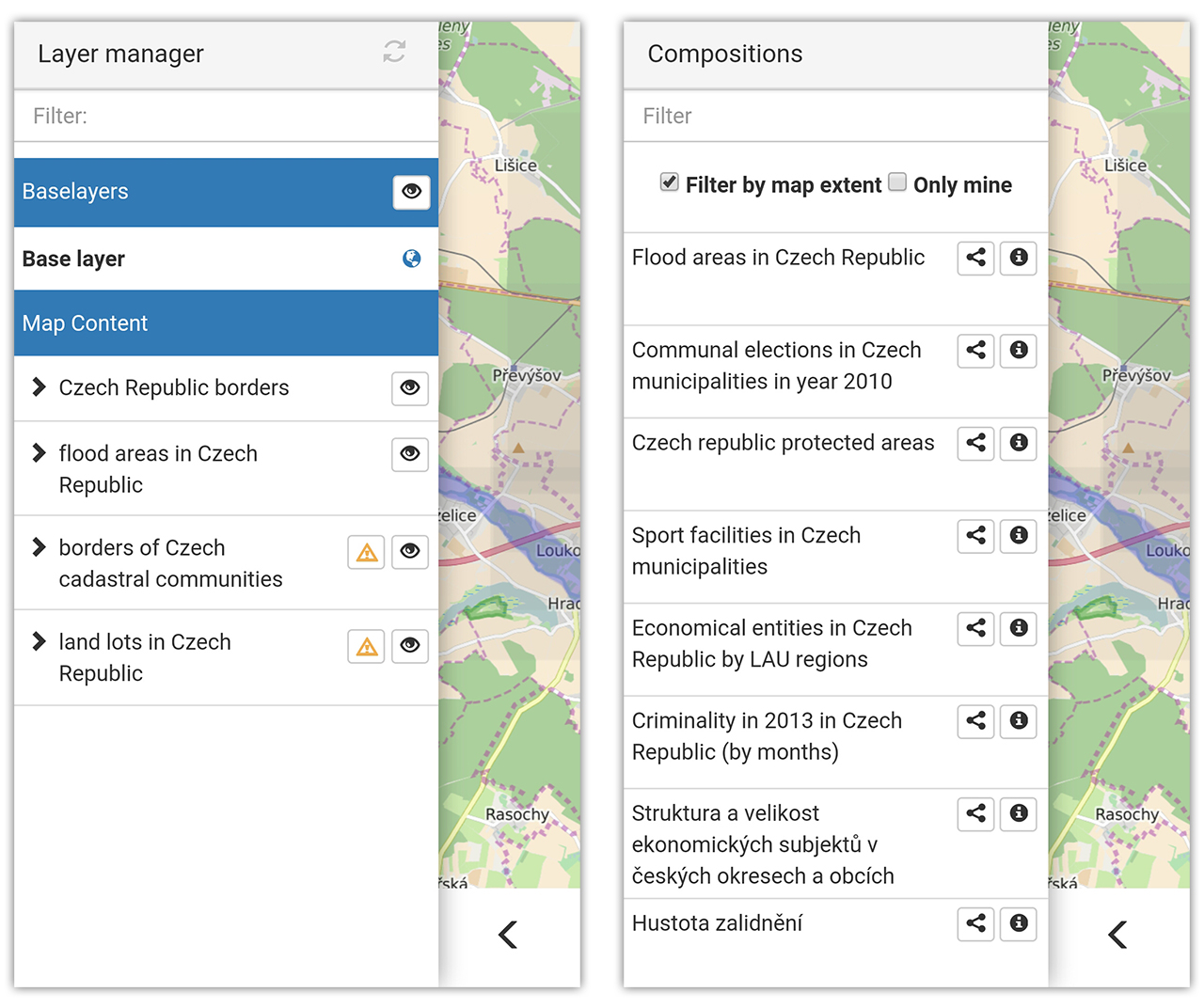
Map Composer
The application is providing the necessary functionality for displaying geographic data on a map and then creating a map composition (a thematic map) that can contain several data layers. After the map composition is created, i.e. detailed definition and metadata of each layer of the composition along with the composition itself, it can be saved as a JSON-styled text document. Then, this document can be read and visualized by an HSLayers NG-based web application. So, the main purpose of the application is to share visualized geographic data between users.
Map Composer is currently it is able to display map layers that come from the following services/sources: WMS, WFS, WCS, KML, GeoRSS, GML, GeoJSON and SOS. A user can then combine the layers he wishes into a composition that will be saved as an .hsl file (JSON styled text document that contains all necessary definitions and metadata of each layer and composition itself). It is further intended that the user will publish the composition he has created and share it with other users. It can be done in several ways: if user sets composition to “public” it can be viewed by other users of the platform in the Thematic Atlas web-application or the user can use Embed Map utility (feature of Thematic Atlas) to generate link to insert the map window with composition into any web-page (as data object, iframe etc.).
In the context of the project the Map Composer is playing very important role as it is allowing thematic map creation. With the help of this application users can overlay data from different sources and visually explore patterns in data and relationships between different data layers. The application is intuitive enough even for users that don’t have strong background in GIS.
Mobile Thematic Viewer
It is mobile version of Thematic Viewer. The mobile application being developed as a part of the SDI4Apps project is a result of the HS-Layers framework and mobile specific code integration. It utilises PhoneGap framework, which packs HTML, CSS3 and JavaScript code into an installation package. Apache Cordova is the software developer uses to compile the application with PhoneGap. Because PhoneGap is based on rendering the application via web view, not the platforms UI framework, the source code does not have to be platform specific and can still benefit from the native device APIs. As the consequence of employing web views, performance and other issues may arise.
One such issue is the fact that Android devices prior to V4.4.3 KitKat uses the default Android browser to render the web view, which does not provide GPU acceleration and restricts CPU support if the application calls for GPU acceleration. This results in severe performance decrease and has to be dealt with. Subsequent Android versions use Chromium for web view rendering, which does support GPU acceleration. The Crosswalk webview plug-in for Cordova solves this issue by incorporating Chromium directly in the application package. That increases the package size by approximately 20 MB, which could be undesirable.
Another matter addressed was usage of proxy service by HS-Layers. The service could not be utilised in the application, because it is written in Python, which is unsupported by Cordova by default. Cordova instead uses domain whitelisting for various types of HTTP requests (images, stylesheets, scripts, etc.), so a simple URL may be used for search queries and JSON or image requests if whitelisted properly. HS-Layers components that make HTTP requests needed to be modified so they make a request with simple URL in the mobile version, but still serve the URL to the proxy service on desktop. A JavaScript mobile variable was defined in the index.html file of the Cordova application and a conditional statement in each component verifies if this variable is defined.
Geolocation component also needed to be rewritten to use native geolocation API via the Cordova Geolocation plug-in. This allows for usage of high precision GPS service. A GPS logging functionality was also introduced as a part of the mobile geolocation component. It employs a WebSQL database to store location information (available values are longitude, latitude, altitude, horizontal accuracy, current velocity and heading). Another storage options are also available, including local file storage or other database types. This logging functionality can be extended to display various statistics about created GPS tracks or the tracks themselves as features on the map. Displaying velocity and altitude as well as centring on the user’s current position functions as intended.
Mobile specific layout was dealt with mainly at the Dresden 2015 hackathon. A CSS stylesheet is used to redefine properties of relevant classes. The mobile toolbar is proposed to be located on the bottom of the screen and to contain only four buttons, namely Layer manager, Search, Geolocation and one specific to each example. This results in a simpler layout that is easier to use on a mobile device than the desktop layout.
Quiz
One of the interesting tasks of the pilot is creating ontologies for those mentioned geographic objects. After creating those ontologies and then storing the data in RDF format and uploading it to Virtuoso, it is possible to query the data based on created ontologies, taking into account different interesting relationships between the classes. This can be very useful as in some cases it is impossible precisely to define some of the relationships by geometrical/topological means or even by visual means.
The semantic to such games brings a lot. It allows to add pictures and description of the places automatically if needed – for example from DB:Pedia. Also as was mentioned below it allows explore various interesting relationships between the objects: rivers and towns, mountains and provinces, lakes and habitats of water bird species, countries and forests, and in questions all these relationships can be combined for example we have following classes: cities, provinces, countries and rivers then we can ask such question ‘find the city with more then 100 000 inhabitants, that lies in x province, on the bank of x river, that flows through x,y,z countries?’. It can well be filled with the picture of the most famous monument from that city from DB:Pedia.
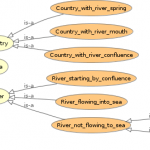
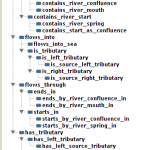
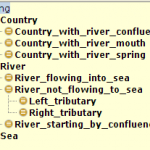
The Apps provides spatial analysis and build semantic linkage among different types of data. Like for example: river A is crossing countries A, B, C. Protected area X is in countries Y. Z. The results of analysis are stored as RDF files, so it allows different types of queries and educational scenarios. The next images show examples of derived ontologies (click to view larger):
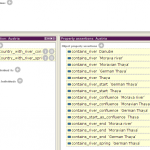
- INSPIRE4Youth: Semantic linkage
- INSPIRE4Youth: Classes
- INSPIRE4Youth: Object properties
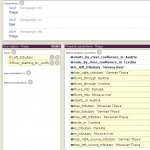
- INSPIRE4Youth: Austria example
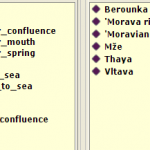
- INSPIRE4Youth: Classes II
- INSPIRE4Youth: Dyje example
This ontologies allows generate number of questions. See basic example: